New features in Trimble Business Center (TBC) offer advanced capabilities that boost efficiency, improve output, and open new markets by including artificial intelligence to streamline classification and feature extraction processes, as well as photogrammetric tools to produce high-accuracy aerial data products.
Investment in geospatial technology is driven by the desire to make better decisions based on complete and accurate information. Continued advances in reality capture data with mobile mapping systems, drones, 3D laser scanners, and other tools create demand for software capable of fully leveraging the data. New capabilities in Trimble Business Center (TBC) integrate artificial intelligence (AI) and connected workflows to facilitate the efficient extraction of information from multiple types of data and connect multiple users to one data management environment that unlocks the true value for a broad range of users.
Responding to industry trends
TBC’s evolution reflects industry trends, such as a shift to doing business in the cloud and widespread demand for faster and more accurate information. New features improve access to data, increase efficiency and productivity, offer better visibility and transparency, and support decision-making by providing more informed insights.
The key focus on integrating diverse data types addresses the surge in mixed-reality applications and the proliferation of various sensors. Capabilities that support processing a wide array of data inputs ensure the platform remains compatible and flexible for all users, aligning with the changing landscape of surveying technology.
The latest enhancements for the office emphasize connected workflows to encourage data sharing throughout the ecosystem. A single source of truth is created by combining various data sets. Integrating data from multiple sources, such as mobile mapping systems, terrestrial scanners, and drones, results in richer and more intelligent deliverables, including accurate 3D models and digital twins that support design and construction projects.
Cloud-based integration is supported by functionality to transfer massive reality-capture data sets. TBC is the only application capable of uploading panoramic imagery and point cloud data from any source as one data set to the Trimble Connect cloud-based common data environment. Within Trimble Connect, multiple desktop and cloud applications from various manufacturers can be used together.
The recently launched Trimble Reality Capture Platform Service (TRCPS), an extension of Trimble Connect, is a secure web-based solution that facilitates effective collaboration among stakeholders, maintains data integrity, and enables multiple platforms to connect to one service. By democratizing access to scanning data, TRCPS helps the geospatial footprint reach a wider audience in the office. Early usage statistics show that for every one person contributing scan data, there are 10 people consuming the data, which extends the utility of point clouds.
When it comes to aerial photogrammetry features, continued development is directly influenced by a commitment to sensor fusion—leveraging multiple sensors within a single solution—to eliminate the need for multiple products.
AI’s growing role in generating data insights
Software is evolving to keep up with advances in hardware that produce massive volumes of data. To fully leverage the new data collection technologies, AI-based feature extraction and classification tools are critical. The pioneering use of AI in data processing is propelling TBC towards incorporating smarter algorithms that can automate routine tasks, enhance data accuracy, and streamline processing times. Meeting the rapidly growing demand for geospatial information in many industries relies on software to enable flexible, customizable automation workflows.
The user already has the ability to generate information for many types of analysis, but AI gives more tool options and faster and better results. This includes AI-based capabilities for automated point-cloud classification, automated extraction of asset geometry and attributes, and complex domain-specific analysis workflows such as stockpile earthwork volume management and pavement condition inspection. Automated processes advance existing workflows and create more powerful tools that require minimum user interaction for monotonous tasks, such as the introduction of an AI model for fully automated extraction of lane lines from mobile mapping data.
Software today offers tools and workflows that satisfy the standard requirements of most surveying and construction projects, but customers with non-standard, unique, domain- or location-specific requirements need additional resources. TBC includes capabilities for custom training of classification AI models and generic CAD point extraction for objects in point clouds from any sensor. By customizing workflows, users can create their own intellectual property (IP) and offer unique and personalized services to their customers, distinguishing themselves in a market where everyone has standard pre-built tools.
Capabilities in practice
- GeoVerra, one of Canada’s most established land surveying and geomatics firms, uses a powerful combination of mobile mapping, AI processing and trained models in TBC to complete transportation projects with speed and precision while setting new standards for project delivery. “We see at least 30 percent time savings on large projects when performing feature extraction and classification in TBC,” says Alex Garcia, GeoVerra’s national manager of mobile solutions. “The comprehensive information generated adds value and helps us meet and often exceed customer expectations.”
At Trimble Dimensions 2024, GeoVerra described how they are leading the way in the transportation industry by utilizing mobile mapping systems for fast, safe, and accurate geospatial data collection. They are also training unique AI models in TBC for classification and extraction of assets in airports, railway and roads for better data accuracy and workflow efficiency.
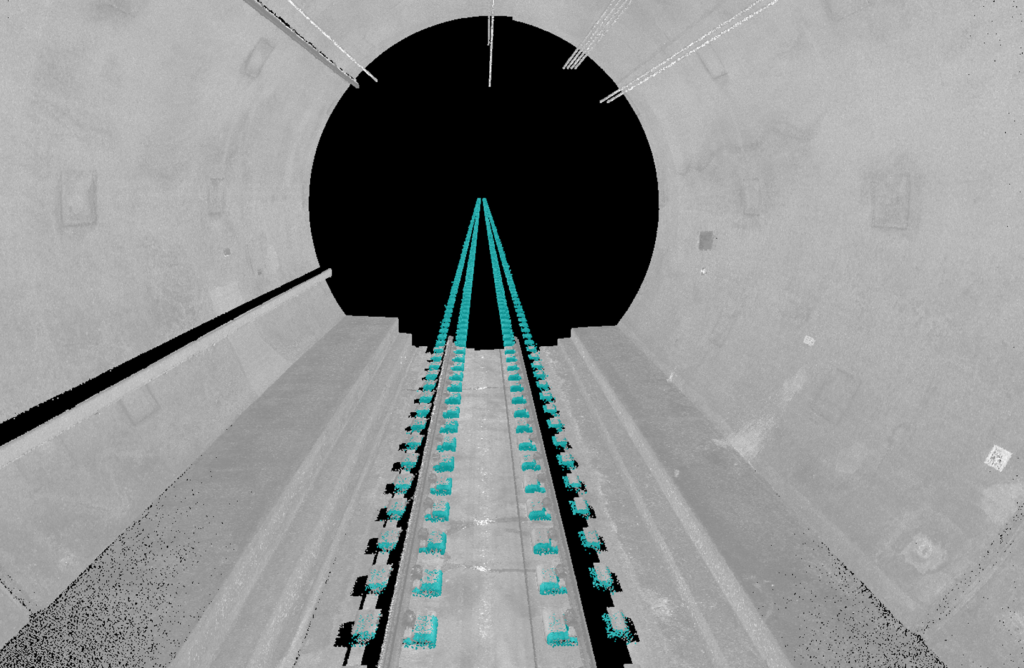
- Rhomberg Sersa Rail Group (RSRG), another innovative technology company, is adopting new methods of monitoring, inspecting and analyzing rail infrastructure during and after construction to improve safety and assist with long-term lifecycle management. At the Gotthard Base Tunnel in Switzerland, AI models in TBC were trained to automatically extract 20,000 rail sleepers (railroad ties) that had been installed in the tunnel, drastically reducing the time needed to identify anomalies.
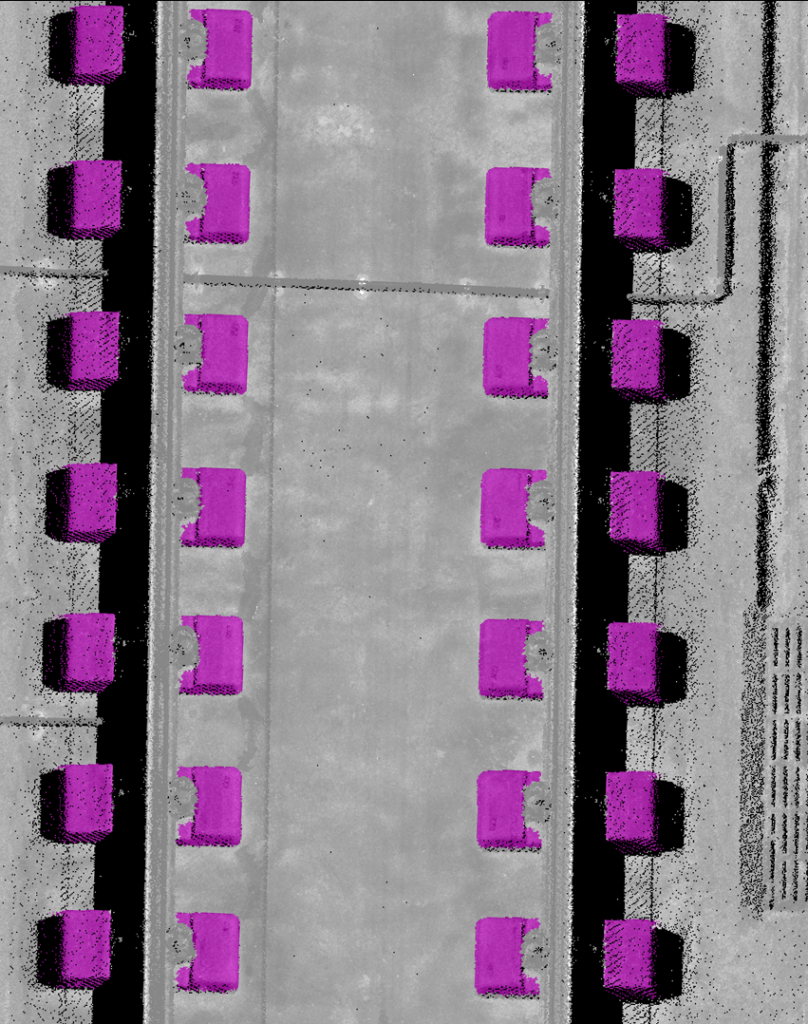

A new tool in TBC software was used to train 3D deep learning models to extract rail sleepers from the point cloud. Photo credit Rhomberg Sersa Rail AG.

Spacing between each pair of sleepers was checked to verify that the gap fell within the required tolerance. Photo credit Rhomberg Sersa Rail AG.
“TBC offered the capability to train AI for a specific type of sleeper and improve the results, which allowed us to automate the extraction process and complete the work quickly with confidence,” said Dimitrios Kyritsis, RSRG’s digital rail services manager. “We were pleased with our 97% accuracy after training the model.”
Transforming pavement and roadway asset inspection
With the goals of improving work zone safety and transportation user safety, and decreasing asset maintenance costs, new end-to-end workflows are changing the way pavement and roadway data is collected and processed. More frequent and detailed condition information is now available through the use of mobile mapping systems and software that turns this data into information.
Vehicle-mounted mobile mapping systems are ideal for large linear projects. Workers safely drive at normal speeds without costly road closures while high-resolution 360-degree cameras and dual laser scanners capture comprehensive information about pavement and roadway assets.
A key area of functionality for the transportation infrastructure industry is the seamless workflow that connects data collection, data processing/information extraction, and management of this information for budgeting and decision-making. TBC automatically extracts information about the location and severity of each pothole and rutting, corrugation, depression, bump, shoulder drop-off, different types of cracking, etc. In addition to detection, TBC evaluates the severity of each defect and ties the location of defects to segments within each analyzed road section.
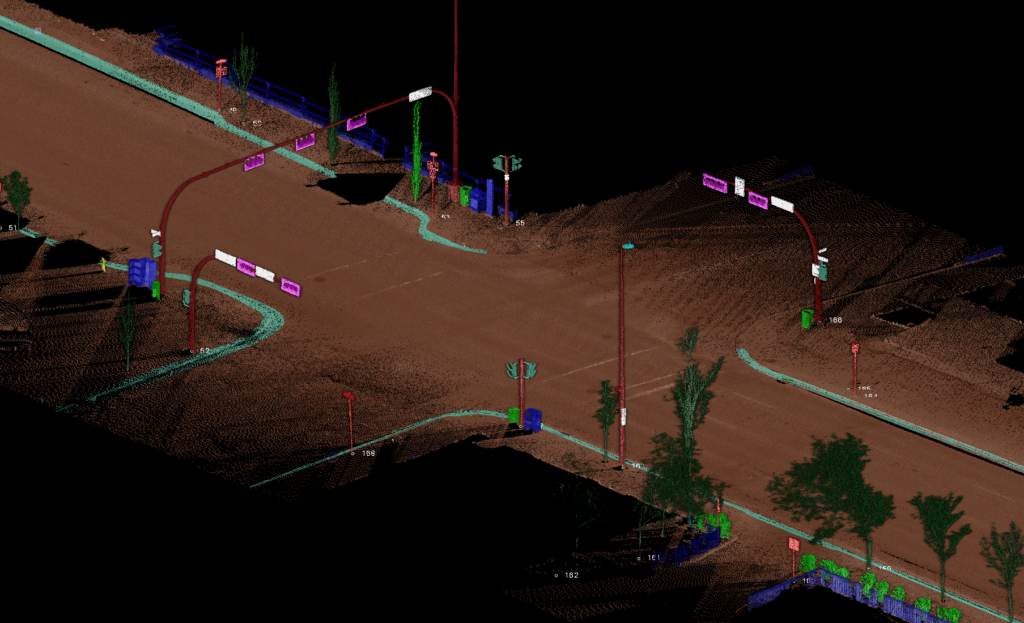
3D deep-learning models were trained to extract features such as curbs, trash cans, traffic lights and sign plates using TBC. Photo credit GeoVerra.
The International Roughness Index (IRI) and Pavement Condition Index (PCI) is calculated for pavement inspection reporting. The condition information can then be consumed by Trimble AgileAssets software, which provides advanced analytics to support data-driven decisions across the infrastructure lifecycle.

Pavement Inspection functionality in TBC automatically extracts distresses and calculates Pavement Condition Index. Photo credit GeoVerra.
The comprehensive pavement management ecosystem allows for efficient data collection, analysis, and management, and supports proactive instead of reactive asset management for additional cost and time savings. Fixing issues before they become driving hazards protects employees and transportation users while decreasing the cost of asset maintenance.
Transportation asset management is an important application area for TBC’s feature extraction and classification tool. By implementing the pavement analysis workflows, users can analyze many miles of pavement significantly faster compared to traditional methods.
Automated AI workflows deliver more granular information with higher accuracy and produce more consistent and objective analysis, producing better results compared to traditional methods. The combination of efficient data collection and AI processing is key to delivering an effective asset management program.
Demand grows for enhanced aerial photogrammetry support
Photogrammetry has become indispensable in surveying. Today, it’s rare to find a surveyor without a drone ready at hand. TBC’s mission is to make integration of drone data into existing projects as straightforward as possible. The platform is designed for ease of use, enabling surveyors to incorporate drone data seamlessly into their daily routines.
The demand for 2.5D and 3D photogrammetry models is expanding across various industries, from construction and urban planning to inspection, data preparation, and monitoring. The TBC team is supporting this need with a commitment to accuracy, automation, and simplicity. By continuously refining TBC algorithms to meet the demand for higher precision, customers have access to state-of-the-art photogrammetric technology.
The photogrammetry module in TBC includes extensive functionality originally developed in Trimble Inpho software. These features support importing data from a broad range of drones and aggregating the aerial data with other survey data to produce comprehensive photogrammetric 3D deliverables.
The processing of drone imagery using the photogrammetry module is effective for complex projects, including those with oblique and nadir imagery. The resulting 3D point clouds and meshes enable the processing of structural inspection projects, such as bridges, open-pit mines and dams.
Bringing more value to data
The shift towards remote work and the need for cloud-based solutions for team collaboration are reshaping surveying workflows. Real-time data sharing, cloud computing, and collaborative project management are just the beginning.
Analysis and report generation are enhanced by the ability to receive data from multiple sources, process that data, and interact with other software within and outside the ecosystem. Whether it’s aerial, terrestrial, mobile mapping, or tunneling data, these tools elevate data processing capabilities, while the connected workflow significantly improves communication and transparency between all stakeholders with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
New AI-based functionality for classification and feature extraction does the heavy lifting to make geospatial professionals more efficient and reliable, while the additions to the photogrammetry module offer advanced processing of aerial imagery for inclusion in 3D models and digital twins. Innovative software truly reveals the value of the data by extracting valuable insights with high accuracy and speed and generating actionable information.
__
 Khrystyna Bezborodova is a feature extraction product manager at Trimble Geospatial. She coordinates teams across Trimble Business Center, Trimble Photogrammetry, eCognition, Mobile Mapping, Scanning and Central AI to deliver point cloud and image-based geometry and attribute deliverables for survey and construction workflows.
Khrystyna Bezborodova is a feature extraction product manager at Trimble Geospatial. She coordinates teams across Trimble Business Center, Trimble Photogrammetry, eCognition, Mobile Mapping, Scanning and Central AI to deliver point cloud and image-based geometry and attribute deliverables for survey and construction workflows.
 Ben Messer is a product manager for Trimble Business Center. His responsibilities include overseeing the development and enhancement of TBC while ensuring that the needs of survey and construction professionals are met. He works closely with the development team and other TBC product managers to prioritize features, gather user feedback, and guide the overall product strategy to deliver a comprehensive office software solution.
Ben Messer is a product manager for Trimble Business Center. His responsibilities include overseeing the development and enhancement of TBC while ensuring that the needs of survey and construction professionals are met. He works closely with the development team and other TBC product managers to prioritize features, gather user feedback, and guide the overall product strategy to deliver a comprehensive office software solution.
 Thomas Widmer is senior product manager for Trimble Photogrammetry. He focuses on the integration of photogrammetric solutions for nationwide aerial image projects (Trimble Inpho) and photogrammetry solutions for the surveying market. Thomas has worked for over 20 years as a support, trainer, and consulting engineer for Trimble Inpho.
Thomas Widmer is senior product manager for Trimble Photogrammetry. He focuses on the integration of photogrammetric solutions for nationwide aerial image projects (Trimble Inpho) and photogrammetry solutions for the surveying market. Thomas has worked for over 20 years as a support, trainer, and consulting engineer for Trimble Inpho.